Retirement Calculator
| Year | Age | Start Balance | Contribution | Investment Return | End Balance |
|---|
Embed this calculator
Adjust the size if needed, then copy the code below into your page or blog. The calculator will load in an iframe and stay updated automatically.
✅ Works on most website builders (WordPress, Elementor, HTML, etc.) · Please keep the credit link to support future free tools.
How can you save for retirement?
How much can you withdraw after retirement?
How long can your money last?
Table of Contents
- What is a Retirement Calculator?
- How Does a Retirement Calculator Work?
- Key Retirement Formulas Explained
- Example Retirement Scenarios
- Factors That Influence Retirement Planning
- Real-Life Applications of Retirement Calculators
- Tips for Effective Retirement Planning
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Retirement Planning Around the World
- Conclusion: Why Retirement Calculators Matter
- Frequently Asked Questions
- References & Sources
🔹 What is a Retirement Calculator?
A retirement calculator is a financial planning tool that helps you estimate how much you need to save to maintain your desired lifestyle after leaving the workforce. By entering your current age, planned retirement age, income, savings, and expected investment returns, the calculator projects how much money you will have at retirement and how long it can last.
Unlike basic savings calculators, a retirement calculator also factors in inflation, contribution rates, and life expectancy. This allows you to test different scenarios and adjust your savings strategy before it’s too late. Whether you’re just starting your career or approaching retirement, these projections give you a clear picture of your financial future.
For example, a person who starts saving early and invests consistently benefits from the power of compounding. Even small monthly contributions can grow significantly over decades, making it easier to reach long-term retirement goals.
🔹 How Does a Retirement Calculator Work?
A retirement calculator works by applying financial formulas to your inputs and projecting your savings growth over time. It combines your income, savings, and expected rate of return with assumptions about inflation and withdrawal patterns to show whether you are on track.
- Current Age & Planned Retirement Age: Defines the saving period before retirement begins.
- Income & Savings Rate: Estimates how much you can save each year based on salary and contributions.
- Investment Return: Projects growth of your savings through compound interest.
- Inflation: Adjusts future values to reflect reduced purchasing power over time.
- Life Expectancy: Helps estimate how long your money must last during retirement.
Using these inputs, the calculator generates a savings projection and a retirement withdrawal plan. You can test different assumptions, such as retiring earlier, saving a higher percentage of income, or lowering expected investment returns, to see how your results change.
🔹 Key Retirement Formulas Explained
A retirement calculator relies on well-known financial formulas to estimate how savings will grow and how much can be withdrawn safely. Below are the key formulas behind the calculations:
1. Compound Growth (Future Value of Savings):
The formula to calculate the future value of savings is:
FV = PV × (1 + r)n + C × [(1 + r)n - 1] / r
Where:
• FV = Future Value of savings
• PV = Current savings
• r = Annual rate of return (as decimal)
• n = Number of years until retirement
• C = Annual contribution
2. Monthly Withdrawal Calculation:
Once you retire, your monthly withdrawal can be estimated as:
Withdrawal = FV ÷ (Years of Retirement × 12)
3. Inflation Adjustment:
To keep results realistic, future values are adjusted for inflation:
Real Value = Nominal Value ÷ (1 + i)n
Where i is the annual inflation rate.
These formulas ensure that projections are not only based on savings growth but also take into account real-world conditions such as rising costs of living. This helps you plan a more sustainable retirement strategy.
🔹 Example Retirement Scenarios
To understand how a retirement calculator works in practice, let’s look at an example. Imagine a person who is 35 years old, earns $70,000 annually, and plans to retire at 67. They currently have $30,000 saved and contribute 10% of their salary each year with an expected return of 6% and inflation at 3%.
| Factor | Value |
|---|---|
| Current Age | 35 |
| Retirement Age | 67 |
| Current Savings | $30,000 |
| Annual Contribution | 10% of salary (~$7,000) |
| Expected Return | 6% annually |
| Inflation | 3% annually |
With these assumptions, the calculator projects that by age 67, the person could have approximately $1,050,000 in retirement savings. If they live until age 85, they may be able to withdraw about $4,800 per month (adjusted for inflation) without running out of money.
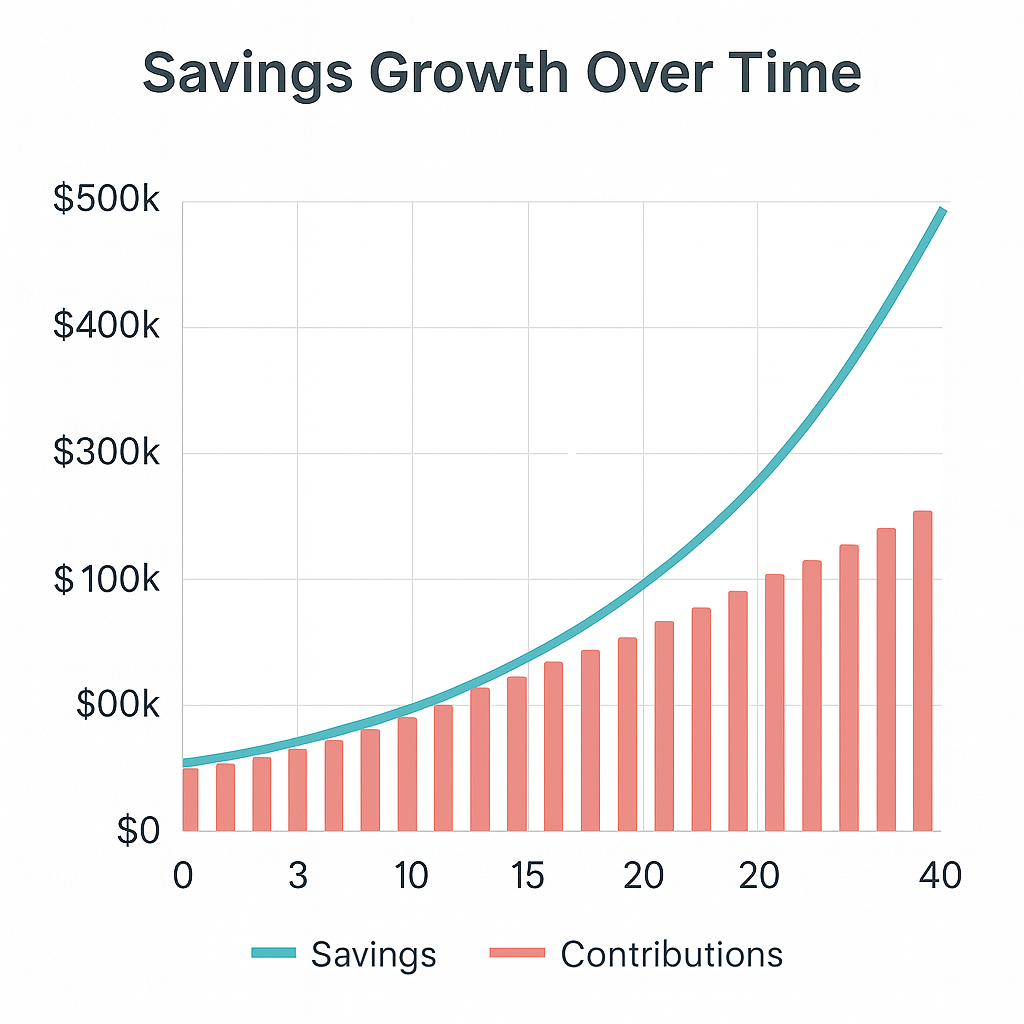
This example demonstrates the power of consistent contributions and compound growth. Even starting with a modest balance, disciplined saving and investment returns can grow wealth significantly over time.
🔹 Factors That Influence Retirement Planning
Retirement planning is not just about saving money — it’s about balancing multiple financial and lifestyle factors that determine whether your nest egg will last. Understanding these influences helps you make smarter, more realistic decisions.
- Income Growth: Higher salaries and career advancement increase your saving capacity.
- Inflation: Rising costs reduce purchasing power, making it essential to plan for higher expenses.
- Investment Returns: Stocks, bonds, and other investments can grow your savings, but returns vary with risk levels.
- Retirement Age: Retiring earlier means fewer years to save and more years to withdraw money.
- Health & Longevity: Longer life expectancy requires more savings to cover medical costs and living expenses.
- Lifestyle Choices: Desired travel, hobbies, and housing will greatly impact how much you need.
These factors are interconnected. For example, delaying retirement by a few years can significantly increase your savings while reducing the total number of withdrawal years, creating a stronger financial cushion.
🔹 Real-Life Applications of Retirement Calculators
A retirement calculator isn’t just a financial model — it’s a planning companion you can use at different stages of your life. People apply these tools in real-world scenarios such as:
- Career Planning: Young professionals estimate how much to save early in their careers to take advantage of compounding.
- Mid-Career Adjustments: Workers in their 40s or 50s evaluate if their savings pace is on track or needs adjustments.
- Pre-Retirement Testing: Individuals nearing retirement model different retirement ages, lifestyles, and income sources.
- Post-Retirement Budgeting: Retirees test safe withdrawal rates to avoid outliving their savings.
For instance, a person planning to retire early at 60 might realize they need to increase their annual contributions or reduce expected lifestyle expenses. Meanwhile, someone with an employer pension can factor this in as guaranteed income, reducing pressure on personal savings.
Tools like our Compound Interest Calculator can also help you visualize how regular contributions grow over time, complementing your retirement planning strategy.
🔹 Tips for Effective Retirement Planning
Retirement planning is most successful when approached early and consistently. Here are some proven strategies to strengthen your financial future:
- Start Early: Even small contributions in your 20s or 30s grow significantly through compound interest.
- Automate Savings: Setting up automatic transfers ensures you stay disciplined and consistent.
- Diversify Investments: Balance risk and return by spreading savings across different assets like stocks, bonds, and ETFs.
- Adjust for Inflation: Plan for rising living costs by choosing realistic growth and inflation assumptions.
- Review Regularly: Revisit your plan every few years or after major life changes such as marriage, new job, or moving countries.
- Delay Retirement if Needed: Working a few extra years can dramatically increase savings while reducing withdrawal years.
Combining these strategies with regular use of a retirement calculator helps you adapt to changing circumstances and stay confident about your long-term financial security.
🔹 Common Mistakes to Avoid in Retirement Planning
Even with good intentions, many people underestimate the challenges of retirement planning. Avoiding the following mistakes can help ensure your savings last as long as you do:
- Starting Too Late: Delaying contributions drastically reduces the power of compound growth.
- Ignoring Inflation: Planning in today’s dollars without accounting for future price increases can leave a funding gap.
- Overestimating Returns: Assuming unrealistic investment performance can lead to disappointment.
- Not Diversifying: Relying too heavily on a single asset class exposes savings to unnecessary risks.
- Withdrawing Too Much: Overspending early in retirement may cause you to outlive your savings.
- Forgetting Healthcare Costs: Medical expenses often rise sharply with age and need to be factored into planning.
By recognizing these pitfalls, you can make smarter decisions and adjust your strategy before it’s too late. A retirement calculator helps highlight the risks and shows how small changes today can make a big difference later.
🔹 Retirement Planning Around the World
Retirement planning looks different depending on where you live. Pension structures, government programs, and cultural expectations all play a role in shaping how individuals prepare for life after work.
- United States: Retirement planning often relies on 401(k) plans, IRAs, and Social Security. Employer contributions and tax benefits encourage long-term savings.
- European Union: Many EU countries provide strong state pension systems, but replacement rates vary. Private pensions and savings accounts are becoming increasingly important.
- United Kingdom: The UK has a state pension but emphasizes additional private and workplace pensions. Auto-enrolment in employer pension schemes has significantly boosted participation.
Despite these differences, one constant remains: personal savings and investment discipline are crucial. State pensions may not fully cover retirement needs, so using tools like retirement calculators is valuable worldwide.
🔹 Conclusion: Why Retirement Calculators Matter
Retirement calculators provide a clear roadmap for your financial future by showing whether your current savings and contributions are enough to sustain your lifestyle after leaving the workforce. Instead of relying on guesswork, you can make informed decisions based on projected outcomes.
They allow you to test different scenarios, such as retiring earlier, saving more aggressively, or adjusting for higher inflation. This flexibility helps you create a plan tailored to your goals and life circumstances.
Ultimately, using a retirement calculator empowers you to take control of your financial future. The earlier you start planning, the more options and security you’ll have when you reach retirement age.
🔹 Frequently Asked Questions
🔹 References & Sources
| Source | Details |
|---|---|
| Investopedia | Comprehensive guide to retirement planning, savings strategies, and key formulas. |
| U.S. Social Security Administration | Official resource on retirement benefits and Social Security income. |
| OECD – Private Pensions | Global insights on pension systems and retirement planning across countries. |
| UK Pensions Regulator | Information about UK workplace pensions, state pensions, and auto-enrolment rules. |
| Calculator.net | Competitor retirement calculator used as reference for structure and features. |
